The Writing Pad
This blog is aimed at helping students of English as a foreign language develop their writing skills.
Saturday
Friday
Five Common Errors
5⃣ Cinco errores (demasiado) comunes en #inglés que todos hemos cometido alguna vez.— Brendan 𝕯𝕸 Ryan 🇮🇪🇪🇸🇪🇺 (@BrendanDMRyan) February 28, 2020
1⃣ In the end vs. at the end
2⃣ To listen to
3⃣ It depends on
4⃣ Present perfect
5⃣ Every day vs. everyday
¿Los reconoces? pic.twitter.com/G24uEmvxJk
Thursday
Essay Connectors Games
Labels:
1º,
2019,
2ºBach,
connectors,
FOR_AGAINST,
game,
opinion,
writing
Sunday
Tuesday
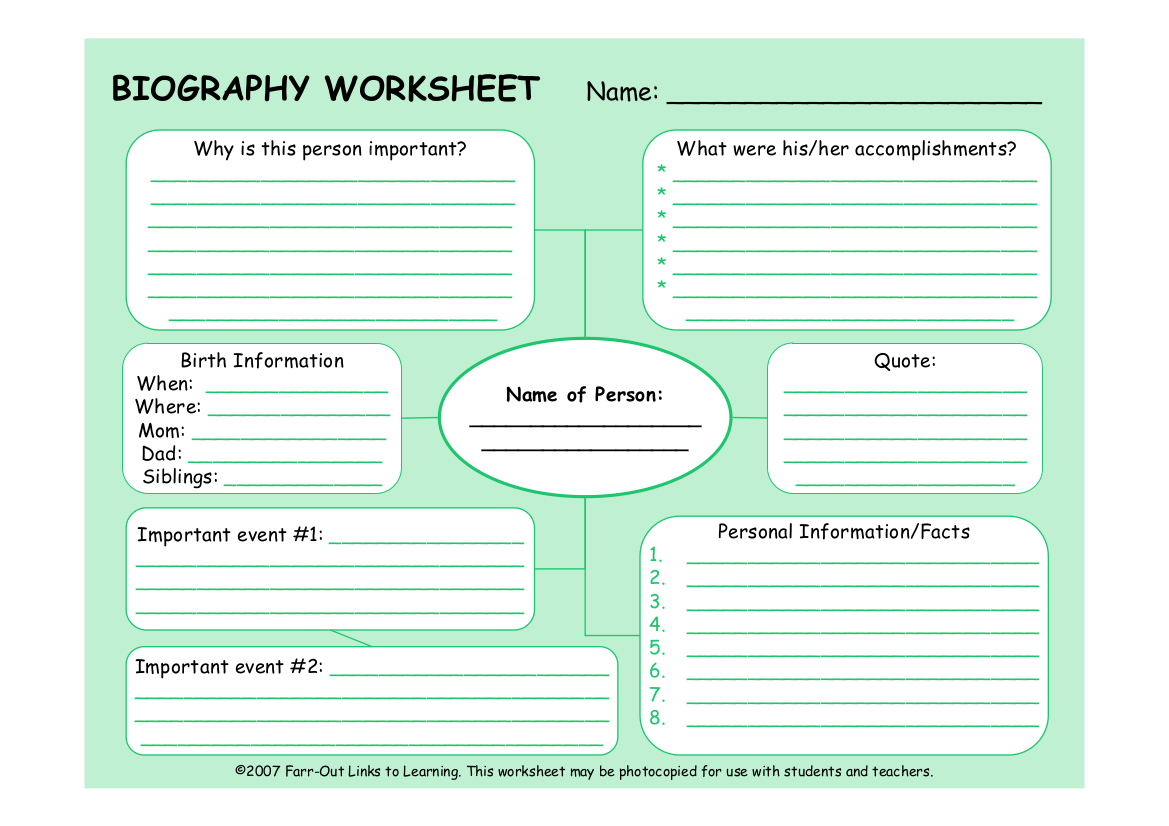
Writing Tasks
UNIT
1
.
WRITE
ABOUT YOURSELF
Name
/ country / year in school / activities you do
UNIT
2
WRITE
ABOUT A PLACE
Name
/ country / When you go / Who you go with / What do you do there
UNIT
3
DESCRIBE
A PERSON
Name
/ hair / eyes / clothes / personality /
something he or she likes doing
UNIT
4
WRITE
ABOUT A COURSE
Course
/ place / days / time / I go with / things we do
UNIT
5
WRITE
ABOUT A PAST EVENT
When?
/ Where? / Who? / What?
UNIT
6
A
STORY
What?
/ Who? / When? / Where? /
UNIT
7
DESCRIBE
A GAME
Name
of the activity / players / starting / rules
UNIT
8
DESCRIBE
A TRIP
Name
of trip / transport / things to see / things to learn / things to visit
UNIT
9
DESCRIBE
A RECYCLING PROCESS
Name
of material / new product / how people make it / how it helps the environment
Saturday
Friday
Saturday
Friday
Saturday
Describing Words
Enter a noun into this website and get a range of words to help you describe it. Superb for creative or descriptive writing projects.
Contrast Words
The words although, though, despite, in spite of and however have very similar meanings; however, they are used in different structures.
Though and although are conjunctions. They go before a clause.
Despite and in spite of are prepositions. They go before a noun or noun equivalent.
However is a transitional adverb. It goes at the beginning of a sentence.
To cut the explanation short, the words DESPITE, IN SPITE OF and BECAUSE OF are followed by a noun phrase or a gerund (verb + ing).
Despite the rain, they went to the beach.
In spite of the rain, they went to the beach.
They didn't go to the beach because of the rain.
The conjunctions BECAUSE, EVEN THOUGH and ALTHOUGH are followed by a clause.
Although it rained, they went to the beach.
Even though it rained, they went to the beach.
Because it rained, they didn't go to the beach.
You can see the explanation again in the following mind map:
Though and although are conjunctions. They go before a clause.
Despite and in spite of are prepositions. They go before a noun or noun equivalent.
However is a transitional adverb. It goes at the beginning of a sentence.
To cut the explanation short, the words DESPITE, IN SPITE OF and BECAUSE OF are followed by a noun phrase or a gerund (verb + ing).
Despite the rain, they went to the beach.
In spite of the rain, they went to the beach.
They didn't go to the beach because of the rain.
The conjunctions BECAUSE, EVEN THOUGH and ALTHOUGH are followed by a clause.
Although it rained, they went to the beach.
Even though it rained, they went to the beach.
Because it rained, they didn't go to the beach.
You can see the explanation again in the following mind map:
Grammar & exercise Exercise 2
but
(bʌt; unstressed bət) conj (coordinating)
1. contrary to expectation: he cut his knee but didn't cry.
2. in contrast; on the contrary: I like opera but my husband doesn't.
3. (usually used after a negative) other than: we can't do anything but wait.
conj (subordinating)
4. (usually used after a negative) without it happening or being the case that: we never go out but it rains.
5. (foll by that) except that: nothing is impossible but that we live forever.
6. archaic if not; unless
sentence connector
informal used to introduce an exclamation: my, but you're nice.
prep
7. except; save: they saved all but one of the pigs.
8. but for were it not for: but for you, we couldn't have managed.
adv
9. just; merely; only: he was but a child; I can but try.
10. informal Scot and Austral and NZ though; however: it's a rainy day: warm, but.
11. all but almost; practically: he was all but dead when we found him.
noun
an objection (esp in the phrase ifs and buts)
1. used as conjunctions
You use although or though to introduce a subordinate clause in which you mention something that contrasts with what you are saying in the main clause. Though is not used in very formal English.
I can't play the piano, although I took lessons for years.
It wasn't my decision, though I think I agree with it.
She wore a coat, even though it was a very hot day.
Don't put 'even' in front of although.
Be Careful!
When a sentence begins with although or though, don't use 'but' or 'yet' to introduce the main clause.
When a sentence begins with although or though, don't use 'but' or 'yet' to introduce the main clause.
Don't say, for example, 'Although he was late, yet he stopped to buy a sandwich'. You say 'Although he was late,
he stopped to buy a sandwich'.
Although he was English, he spoke fluent French.
Though he hadn't stopped working all day, he wasn't tired.
Be Careful!
Don't use although or though in front of a noun phrase. Don't say, for example, 'Although his hard work, he failed his exam'. You say 'In spite of his hard work, he failed his exam' or 'Despite his hard work, he failed his exam'.
Don't use although or though in front of a noun phrase. Don't say, for example, 'Although his hard work, he failed his exam'. You say 'In spite of his hard work, he failed his exam' or 'Despite his hard work, he failed his exam'.
In spite of poor health, my father was always cheerful.
Despite her confidence, Cindy was uncertain what to do next.
2. 'though' used as an adverb
Though is sometimes an adverb. You use it when you are making a statement that contrasts with what you have just said. You usually put though after the first phrase in the sentence.
Fortunately though, this is a story with a happy ending.
For Ryan, though, it was a busy year.
I can't stay. I'll have a coffee though.
Although is never an adverb.
Thursday
Connectives Games
Today we take a look at some words that you can use to link connect short sentences together. Exercise.
Spin the wheel and write a sentence using the selected connective.
Examples of connectives/conjunctions
Spin the wheel and write a sentence using the selected connective.
Examples of connectives/conjunctions
Sunday
Both, Either & Neither
¡Buenos días! Con estos sencillos ejemplos resolvemos las dudas con el uso se BOTH.NEITHER, EITHER. Esperamos que os sea útil 😎.#FelizLunes pic.twitter.com/S3W9HUDWPW— Cambridge Spain (@CambridgeSpain)
To learn more, click on the pic below
Monday
Thursday
For and Against Essays
CLICK THE IMAGES BELOW IF YOU WANT TO LEARN MORE
Ex 1 Ex 2
Writing
Essay writing gap-fill exercise: Has new technology had a positive or negative influence on our lives?
Sunday
Don'ts
Don’t use “nite,” “tho,” or “thru” on essays for school. 🙅🏻♀️— The YUNiversity (@The_YUNiversity) March 18, 2018
💁🏻♂️ Write *night*, *though*, and *through* instead. pic.twitter.com/TRs5bz8f2f
Thursday
Sunday
Writing Opinion Essays
An opinion essay is a formal piece of writing. It requires your opinion on a topic, which must be stated clearly, giving various viewpoints on the topic supported by reasons and/or examples. You should also include the opposing viewpoint in another paragraph.
Wednesday
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)